Content Security Policy (CSP)
Examples
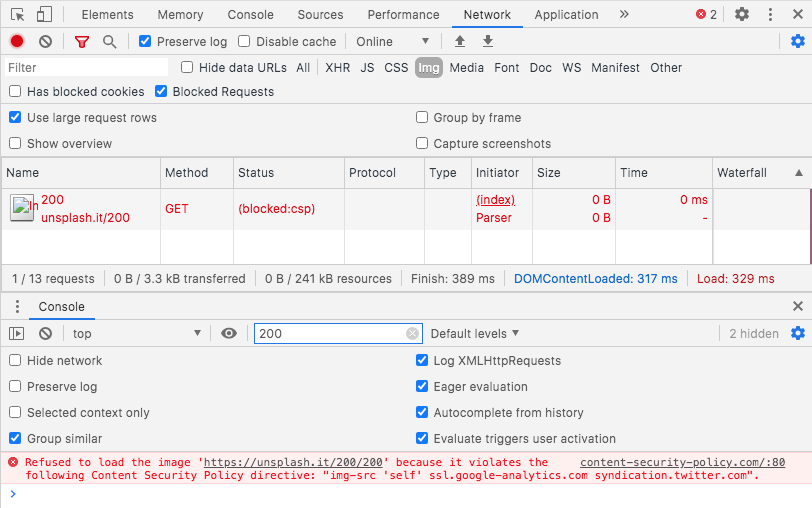
CSP Blocked Loading of Resources
blocked:csp mean?What does blocked:csp mean?
You may be seeing blocked:csp in Chrome developer tools when the browser is trying to load a resource. It might show up in the status column as (blocked:csp)
CSP stands for Content Security Policy, and it is a browser security mechanism. Developers can set CSP using either a HTTP response header, or with a HTML meta tag.
What does an CSP policy look like?
Here's a very simple CSP policy that uses the default-src directive:
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'
With this policy the default-src directive is set to the source list value: 'self'
The default-src directive controls what URLs are allowed to be used for fetching resources on the page. This includes all types of resources such as images, css files, javascript files, etc.
The 'self' value here tells CSP that the browser should only fetch resources from the same origin as the page that set the policy. So if we put that CSP policy on a page located at: https://example.com/page.html then with this policy we can load resources (images, js, css, etc) from https://example.com/*
So if we had an image loading from a url like: https://images.example.com/logo.png
<img src="https://images.example.com/logo.png">
That image would be blocked by CSP, and we may see blocked:csp in the Network tab of Chrome Developer tools. You would also see a message like this output in the Chrome Developer Tools Console:
Refused to load the image 'https://images.example.com/logo.png' because it violates the following Content Security Policy directive: "default-src 'self'"
In FireFox the image request blocked by CSP doesn't show up in the Network tab, but it will output a message to the developer tool console, such as:
Content Security Policy: The page’s settings blocked the loading of a resource at https://images.example.com/logo.png (“default-src”).
So if we wanted to load such an image, we would have to alter the policy to something like this:
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src https://images.example.com 'self';
There are CSP directives for each of the types of resource you want to load (for example img-src, script-src, style-src, etc). Check out this CSP reference for a full list of all the directives and values you can use.
You can see a similar example of CSP blocking an image in our CSP Browser Test.
Why is it blocked in some browsers but not others?
Not all browsers support CSP, for example Internet Explorer doesn't support it. Firefox, Chrome and Edge all have very good support for CSP. Safari support is pretty good, but it may not support the latest features of CSP. So you may see CSP blocking a resource due to differences in implementation, or browser support as well.
Learning more about CSP
Check out the Content Security Policy reference or take a look at more CSP Examples.
CSP Developer Field Guide
Want to learn the ins and outs CSP? Grab a copy of the CSP Developer Field Guide. It's a short and sweet guide to help developers get up to speed quickly.
Grab a CopyStruggling to stay on top of security advisories?
Advisory Week is a weekly roundup of all the security advisories published by the major software vendors.
